Gout and kidney stones are two common health issues that can cause significant discomfort and pain. While they are distinct conditions, there is a fascinating connection between them that is essential to understand. This article delves into the relationship between gout and kidney stones, their causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
What is Gout?
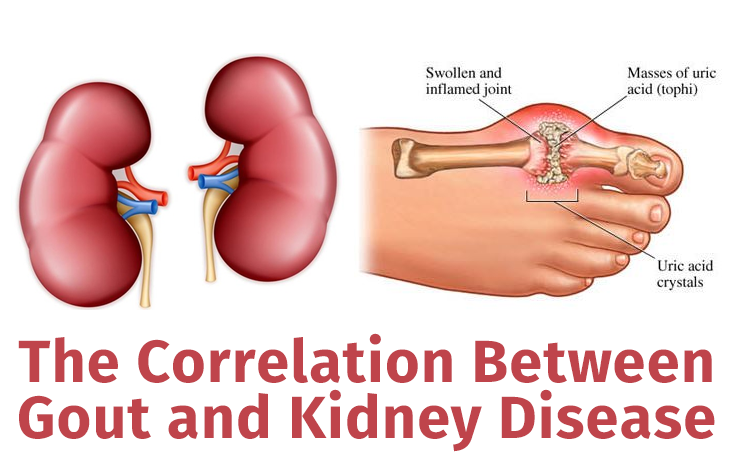
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by sudden, severe pain, swelling, and redness in the joints, often starting in the big toe. It occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints. This excess uric acid can also contribute to the development of kidney stones.
What are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard mineral and salt deposits that form in the kidneys. They can vary in size and can cause severe pain when they move through the urinary tract. There are different types of kidney stones, but uric acid stones are particularly associated with gout.
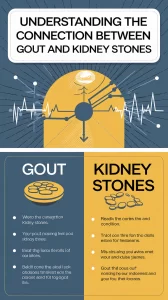
The Connection Between Gout and Kidney Stones
- High Uric Acid Levels:
- The primary connection between gout and kidney stones is high levels of uric acid. Individuals with gout often have elevated uric acid levels, which can lead to the formation of uric acid stones in the kidneys.
- Dietary Factors:
- Certain foods can increase uric acid levels, leading to both gout attacks and kidney stones. High-purine foods (such as red meat, organ meats, and seafood) and excessive alcohol intake can contribute to the development of both conditions.
- Dehydration:
- Dehydration can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of both gout and kidney stone formation. Proper hydration helps dilute uric acid and prevents the crystallization that leads to stone formation.
- Obesity:
- Being overweight is a significant risk factor for both gout and kidney stones. Excess body weight can lead to higher uric acid levels and increased risk of stone formation due to altered kidney function.
- Metabolic Syndrome:
- Individuals with metabolic syndrome—characterized by obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels—are at increased risk for both gout and kidney stones.
Symptoms to Watch For
- Gout Symptoms:
- Sudden and intense pain in joints
- Swelling and redness in affected areas
- Limited range of motion
- Kidney Stone Symptoms:
- Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen
- Blood in urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urination or a burning sensation during urination
Management and Prevention
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help dilute uric acid and prevent kidney stones.
- Monitor Diet:
- Limit high-purine foods, reduce alcohol intake, and incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the risk of both conditions.
- Medications:
- If you have gout, your doctor may prescribe medications to lower uric acid levels. For kidney stones, medications may help dissolve certain types of stones or prevent new ones from forming.
- Regular Check-ups:
- Regular visits to your healthcare provider can help monitor uric acid levels and kidney health, allowing for timely intervention if needed.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the connection between gout and kidney stones is essential for managing your health. By adopting a proactive approach—staying hydrated, monitoring your diet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle—you can reduce your risk of developing these painful conditions. If you experience symptoms of gout or kidney stones, consult your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
✨ #Gout #KidneyStones #HealthEducation #WellnessTips #PreventativeCare #Hydration #HealthyDiet #UricAcid #ArthritisAwareness #KidneyHealth #ChronicPain #LifestyleChanges